Trigonometry Primer
(learning to love triangles)
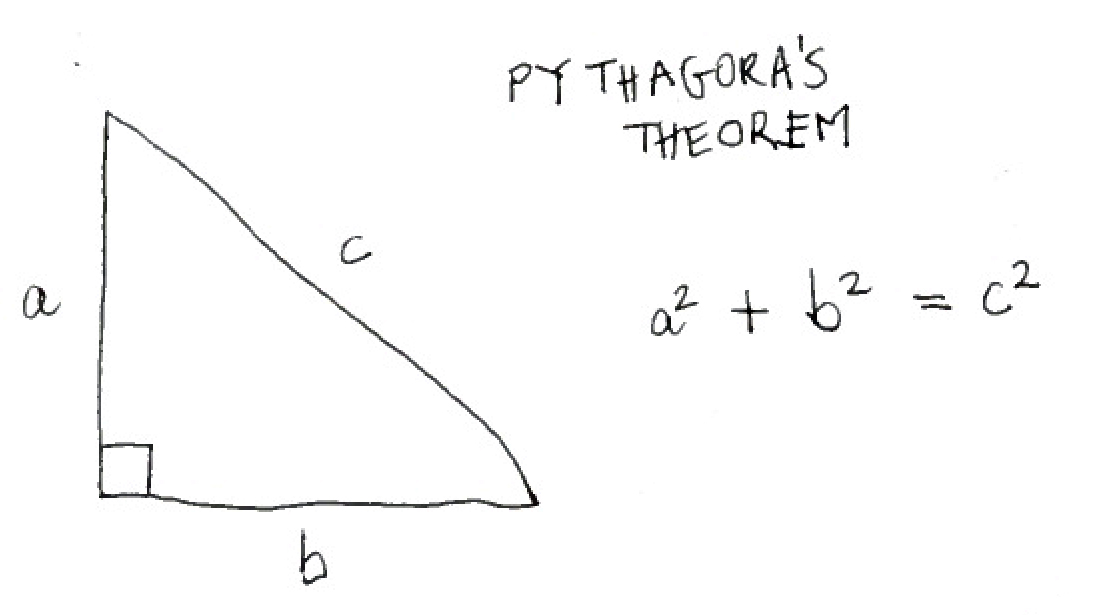
Pythagoras Theorum
Trigonometry is a branch of geometry that is fundamental to all graphics programming. It provides useful equations that enable you to figure out distances between points and how curves and circles can be described in Cartesian coordinates. Remember Cartesian coordinates are points described by x and y values. Trigonmetry also enables you to do things like move shapes in circular motion or oscillate values smoothly back and forth between two extremes.
The right angled triangle is one of the most important parts of trigonometry and Pythagoras was a guy who got pretty famous for figuring out a theorem that relates the length of each of its sides. Pythagora figured out that in every right hand triangle, if you square each of the two shortest sides, their sum equals the square of the longest side.
Right angled triangles are special also because each of their angles has a specific relationship to the ratio between the length of two of their sides. This is what sine, cosine and tangent functions describe. Sin cos and tan are known as trigonometric functions and they give us the relationship between the ratio of two of the triangle’s sides and one of the angles of the triangle. You may recall the acronym: SOH-CAH-TOA that helps you remember how sinθ, cosθ and tanθ relate to the ratio of which of the triangle’s sides.
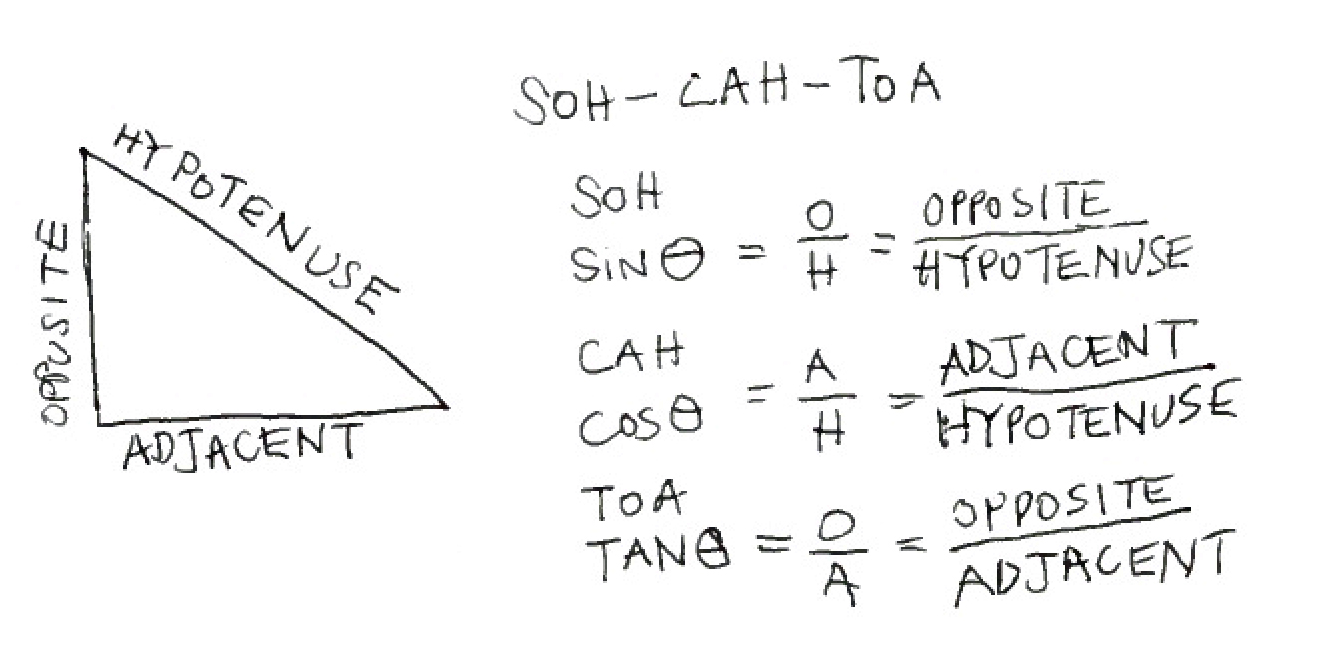
This is all pretty great, because is means that with just a couple of pieces of information about a right angled triangle, like knowing two of its side lengths or maybe knowing one of its angle and a side length, you can use Pythagora’s theorem in combination with the sin, cos and tan equations to figure out everything else.
These triangles are also helpful as they help us to map and understand the x and y coordinates of points along curves and circles. Notice how in the drawing below you can see how any point on a circle will have a relationship to a right angled triangle. This relationship means that a point on a circle can be understood in two ways. Firstly, as we have seen a point can be described by Cartesian coordinates which are of course, by x and y co-ordinates, but it can also be described using polar coordinates. Polar coodinates are an angle and a distance from the origin (the radius of the circle).
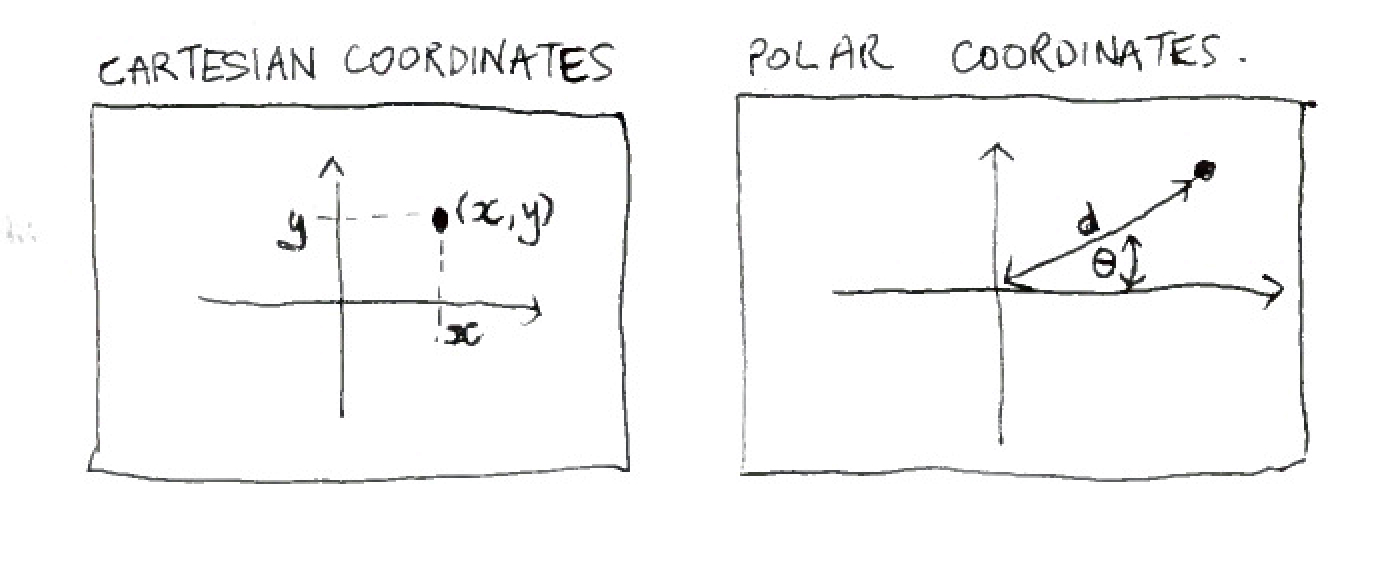
Polar Coordinates
Polar coordinates describe a point using an angle and a distance from the origin. This is useful when you are coding something like an analog clock. When drawing a clock, you would need to place each hand at a particular angle, for example, 3pm is at zero degrees and midday is at 90 degrees. Each hand would be coded as a line drawn onto a screen, that connects two points. So these hand would connect the origin to the x,y coordinates that is at the position of the time. Putting anything on a screen always requires you to describe it in terms of x and y.
So how do we convert between polar coordinates and x-y coordinates?
The relationship between polar coordinates and x,y coordinates can be calculated using a unit circle. This is a circle that has a radius of 1 unit which is useful because it means the hypotenuse in your right angled triange is always 1.
